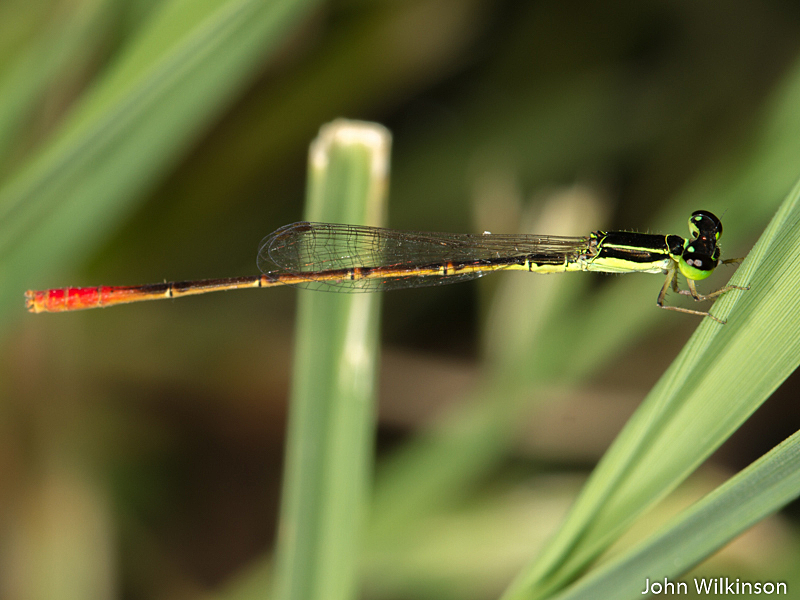
View the above photo record (by John Wilkinson) in OdonataMAP here.
Find the Little Wisp in the FBIS database (Freshwater Biodiversity Information System) here.
Family Coenagrionidae
Agriocnemis exilis – LITTLE WISP
Identification
Very small size
Length up to 20mm; Wingspan attains 27mm.
Most like Agriocnemis pinheyi (Pinhey’s Wisp). They are similar in size, and are in fact the two smallest damselflies in the region. Pinhey’s Wisp has an unbroken green line across the face and an incomplete green line across the prothorax. The Little Wisp shows the exact opposite, having a broken green moustache and an unbroken green line on the prothorax.
Females are variable and best told by their association with the males.
Click here for more details on identification.

Selinda, Botswana
Photo by Ryan Tippett
Habitat
Inhabits dense grass and sedge margins of pools, dams, marshes and floodplains, as well as the fringes of slow moving streams. Generally found at lower altitudes than Agriocnemis pinheyi.

Photo by Ryan Tippett
Behaviour
Usually perches near vertically on a sedge or grass stem. Typically low down close to the water. Unobtrusive and easily overlooked.
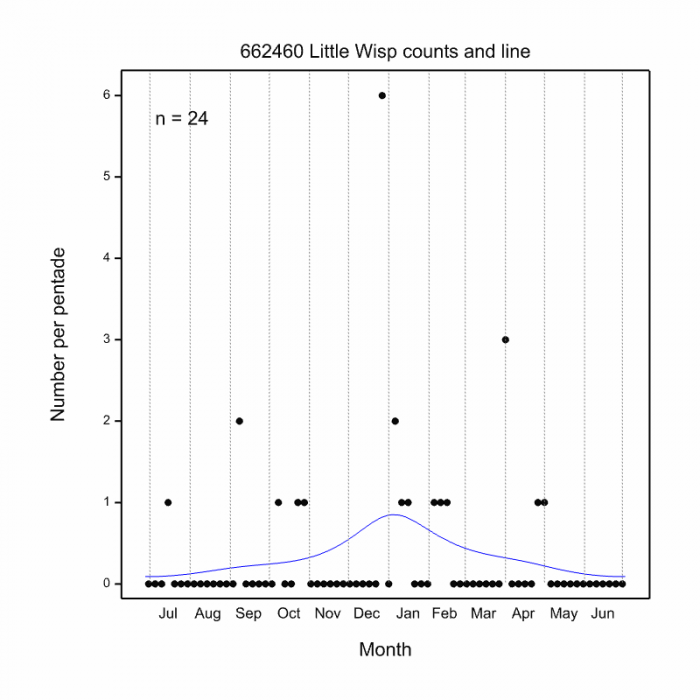
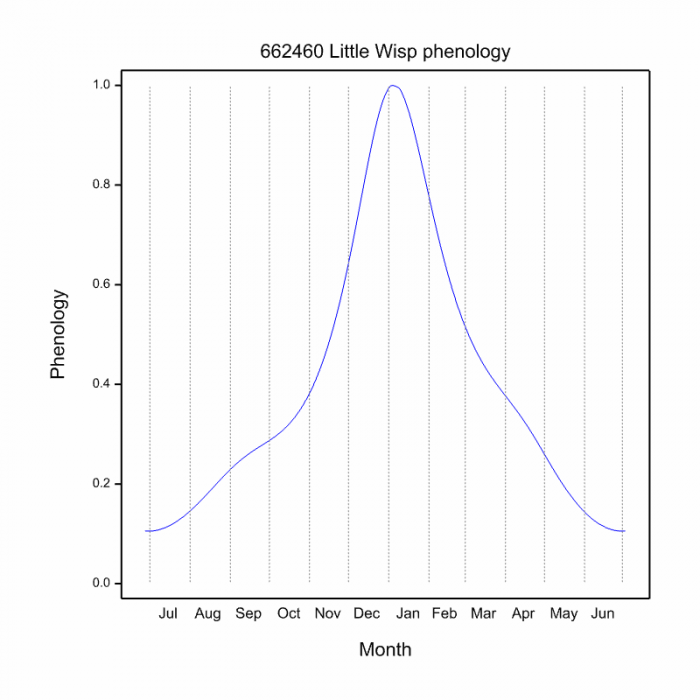
On the wing from November to March (see Phenology below).
Status and Conservation
Fairly common but localised. Listed as of Least Concern in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
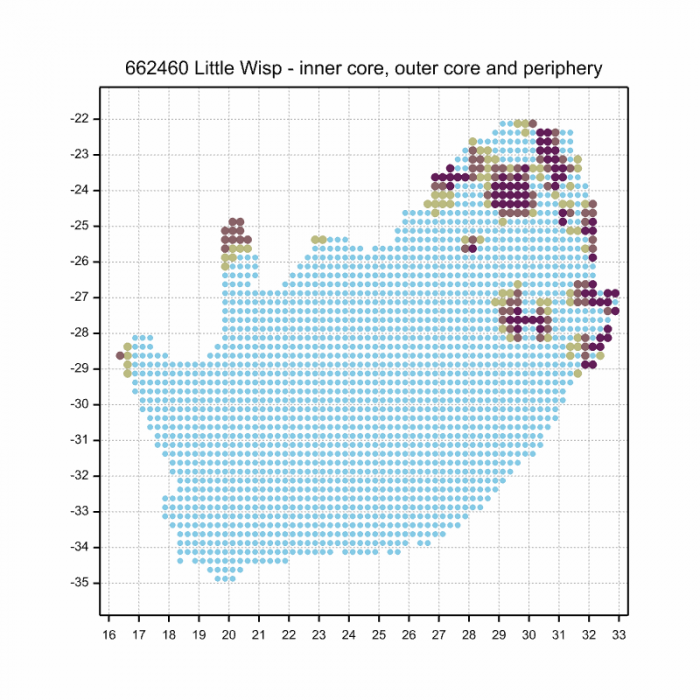
Distribution
Widespread throughout most of Sub-Saharan Africa.
In South Africa it is restricted to the North-East, where it ranges from Limpopo down to coastal NE KwaZulu-Natal.
Below is a map showing the distribution of records for Little Wisp in the OdonataMAP database as at February 2020.

The next map below is an imputed map, produced by an interpolation algorithm, which attempts to generate a full distribution map from the partial information in the map above. This map will be improved by the submission of records to the OdonataMAP section of the Virtual Museum.
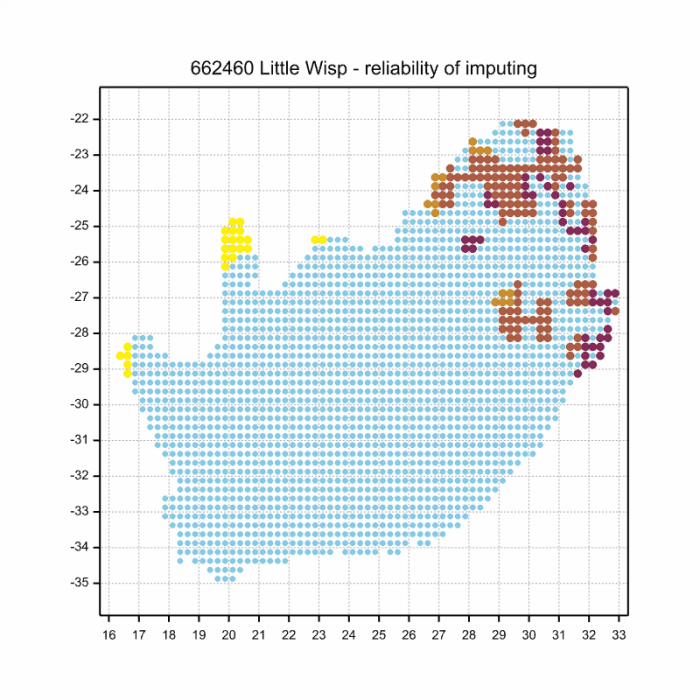
Ultimately, we will produce a series of maps for all the odonata species in the region. The current algorithm is a new algorithm. The objective is mainly to produce “smoothed” maps that could go into a field guide for odonata. This basic version of the algorithm (as mapped above) does not make use of “explanatory variables” (e.g. altitude, terrain roughness, presence of freshwater — we will be producing maps that take these variables into account soon). Currently, it only makes use of the OdonataMAP records for the species being mapped, as well as all the other records of all other species. The basic maps are “optimistic” and will generally show ranges to be larger than what they probably are.
These maps use the data in the OdonataMAP section of the Virtual Museum, and also the database assembled by the previous JRS funded project, which was led by Professor Michael Samways and Dr KD Dijkstra.
Phenology